Reaction mechanisms
There are several reaction mechanisms available - all developed and optimised by our team.
Chemiluminescence (ChemLum2012)
A reaction mechanism for prediction of OH*, CH* and C2* chemiluminescent species
- Detection of non-intrusive OH*, CH* and C2* species is frequently used in the diagnostics
- A reaction model of such species enables direct comparison to their measurements in various combustion environments
- Mechanism supplied with the C1-C4 chemistry from 2012, however independent use of only chemiluminescence chemistry possible

Downloads
Reference
Kathrotia, T. et al., Experimental and numerical study of chemiluminescent species in low-pressure flames. Appl. Phys. B 2012 107, 571-584.
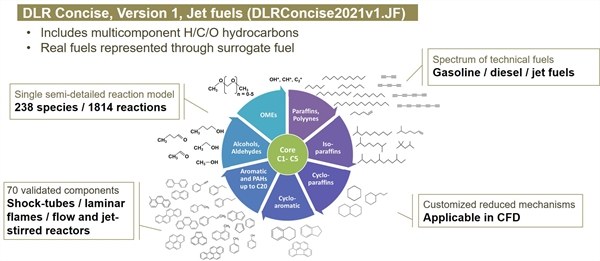
DLR Concise
Version 1, 2021, Jet fuels (DLRConcise2021v1.JF)
A compact reaction mechanism for H/C/O neat components and fuel surrogates
- A single semi-detailed reaction mechanism enables modeling combustion chemistry of spectrum of real fuels represented through surrogate fuels
- Customized reduction possible for CFD applications
Downloads
Reference
Kathrotia, T.; Oßwald, P.; Naumann, C.; Richter, S.; Köhler, M., Combustion kinetics of alternative jet fuels, Part-II: Reaction model for fuel surrogate. Fuel 2020, 302, 120736
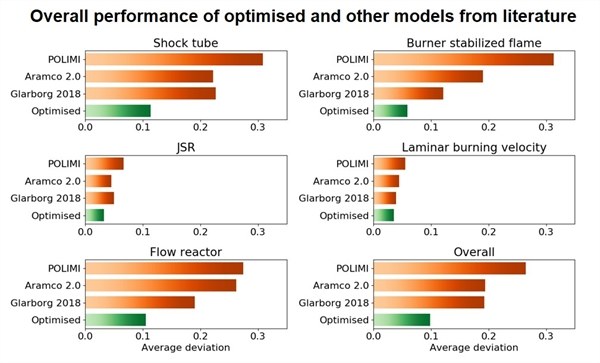
DLR SynNG
Version 1, 2020, Syngas and Natural Gas (DLR SynNG)
An optimised reaction mechanism for mixtures of H2, C1- and C2-species.
- Optimised to match data from multiple experimental types with a broad range of boundary conditions
Downloads
Reference
Methling, T.; Braun-Unkhoff M.; Riedel U., An optimised chemical kinetic model for the combustion of fuel mixtures of syngas and natural gas. Fuel 262 (2020): 116611.
