Pneumatic probes are used to analyse flow fields in wind tunnels for turbomachinery and turbomachinery components such as cascades or other aerodynamic systems. Since velocities and flow angles cannot be measured directly with these probes, and inaccuracies occur in the manufacture of the probe heads, the probes must be carefully calibrated in homogeneous, stationary flow fields with known characteristics. This is the only way to reliably obtain highly accurate measurement results. A major advantage of the probe calibration channel at the DLR Institute of Propulsion Technology in Göttingen is that Mach number and Reynolds number can be set independently over a wide range to suit the particular application of the probes.
The measuring section of the probe calibration channel consists of a free jet within a closed chamber. The large cylindrical chamber is accessible from two sides and can accommodate probes with shaft lengths up to approximately 1000mm.Shifting units driven by stepper motors allow the probes to be adjusted in three directions and by two angles, the angle of attack and the yaw angle. Easily interchangeable axisymmetric nozzles with an outlet diameter of approximately 50 mm can cover a wide Mach number range from sub- to supersonic flow up to approximately Mach 1.8. A 100mm outlet nozzle is available for low Mach numbers down to about 0.2. The total inlet pressure is independent of the Mach number and can be adjusted between ≈ 30 kPa and ≈ 140 kPa.
temperature. The average contraction ratio from the stilling chamber to the nozzle outlet is approximately 16. Sieves and rectifiers in the stilling chamber ensure a uniform and low-turbulence flow field. A diffuser with an adjustable insert is connected to the free jet for pressure recovery. Two windows in the measurement chamber also allow the use of optical measurement techniques such as schlieren or particle image velocimetry.
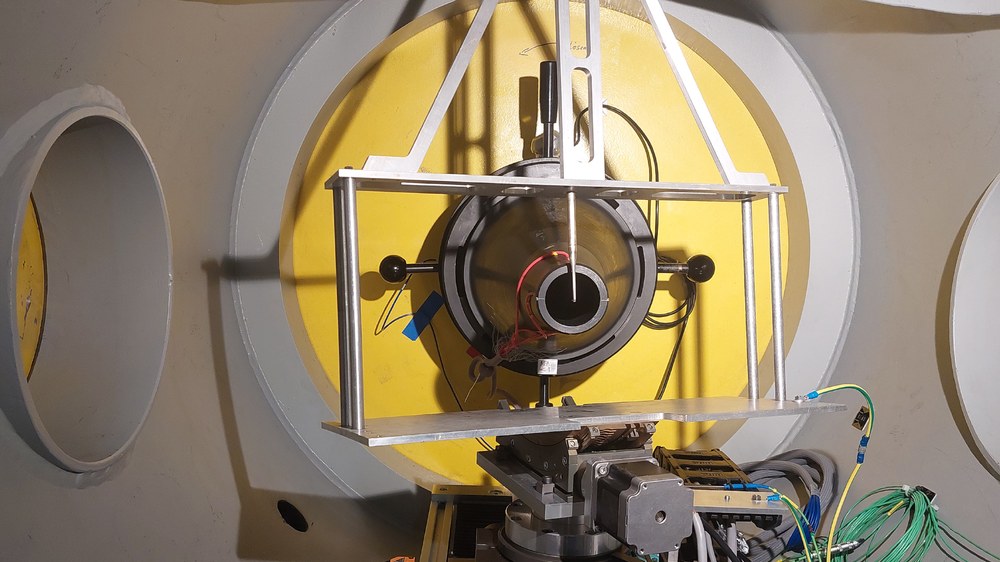

Characteristics of the test bed
Coverage from subsonic to supersonic
Independent adjustment of Mach number and Reynolds number
Adjustment of angle of attack and Gier angle
Research topics
Calibration of flow field measurement probes

