EnMAP enters the Era of Big Data for Hyperspectral Foundation Models
A novel hyperspectral data product from the EnMAP satellite mission is readily available for geospatial analytics through EOC Geoservice. Based on, the dataset SpectralEarth for hyperspectral foundation models is provided, cf. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2408.08447.
The Earth Observation Center (EOC) introduces two novel datasets to the EnMAP user community. Both datasets will significantly add to the utilization of EnMAP data for machine learning and Big Data processing. A level-2A Analysis Ready Data (ARD) collection has been systematically processed by the EnMAP’s Ground Segment processing chain employing the latest atmospheric correction over land processor. Based on this data collection, a 3.3 terabytes dataset of over half a million hyperspectral image patches of size 128x128 pixels and 202 channels has been assembled: “SpectralEarth” aims to share a valuable asset for the training of hyperspectral foundation models and self-supervised machine learning algorithms. To that end, SpectralEarth ships with a subset of annotations for various land cover classification tasks. Both datasets are readily accessible for download upon registration at the EOC Geoservice.
The Environmental Mapping and Analysis Program EnMAP is a German hyperspectral satellite mission with 224 spectral bands that monitors and characterizes the Earth’s environment on a global scale. EnMAP delivers rich information on the status and evolution of terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems to support environmental science and monitoring applications, land cover management, and governance.
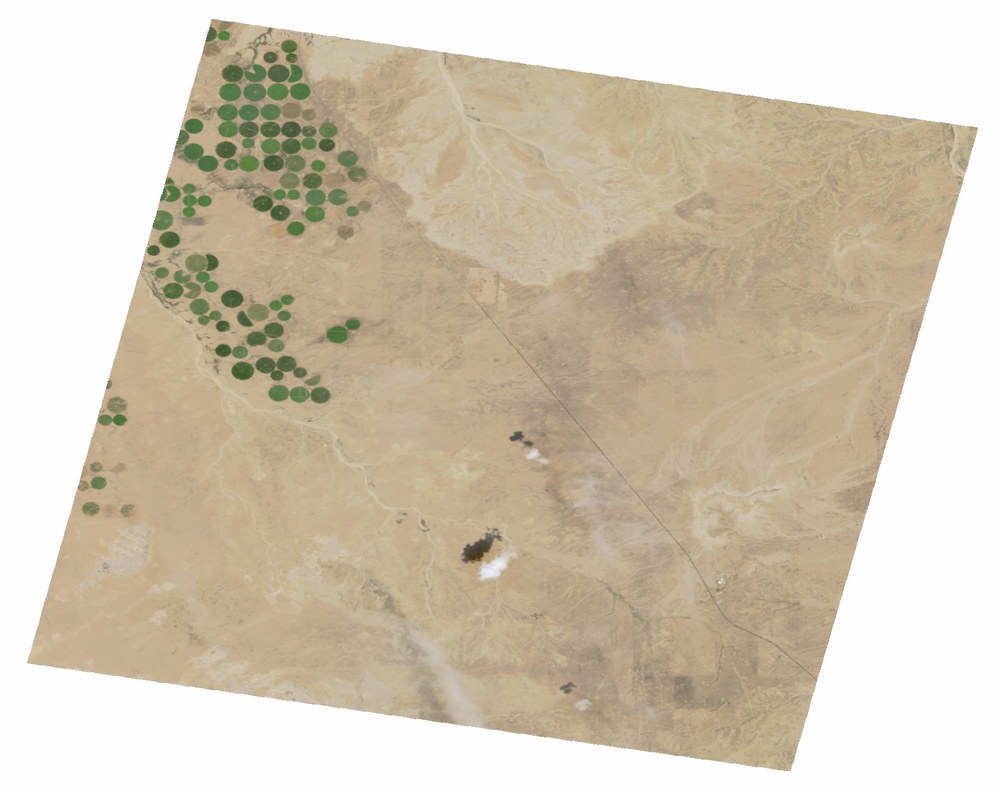

The EnMAP mission ground segment user interface allows for tasking, ordering, on-demand processing, and delivery of EnMAP data at L1B, L1C, or L2A processing levels. The standard user interface for tasking new EnMAP acquisitions is the EnMAP Instrument Planning Portal, whereas the EOWEB GeoPortal provides on-demand ordering of archived data. Both options enable users to specify individual processing parameters. However, many users, in particular those from the artificial intelligence and machine learning community, prefer a standardized data set for Big Data analytics and time series modeling over ordering single data products. Hence, a standardized, consistent, systematically processed, and cloud-native L2A dataset series for the entire EnMAP mission has been processed. It is constantly updated with new data acquisitions. Corresponding metadata follow the CEOS Analysis Ready Data (CEOS-ARD) framework. We provide a Jupyter Notebook to the users as a starter. It covers how to easily and efficiently discover and access the novel dataset via the Geoservice STAC API.
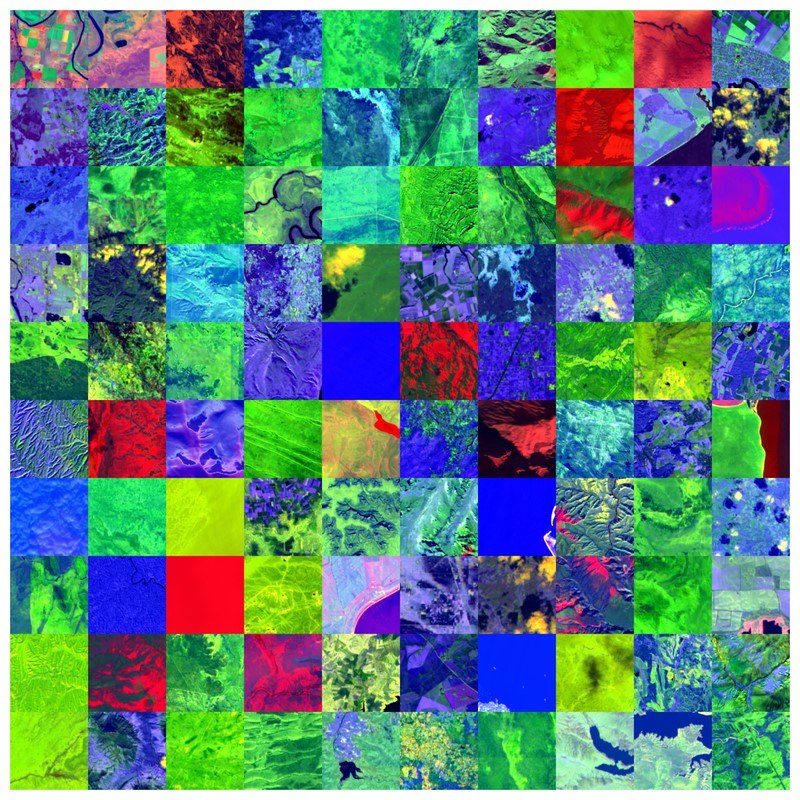
Foundation models have triggered a paradigm shift in computer vision. They are increasingly being adopted in remote sensing, particularly for multispectral imagery. Yet, their potential in hyperspectral imaging (HSI) calls for comprehensive and globally representative hyperspectral datasets. To close this gap, we provide SpectralEarth, a large-scale multi-temporal dataset designed to pretrain hyperspectral foundation models. SpectralEarth is funded by the EU project EvoLand, and it comprises over 538,000 non-georeferenced image patches covering 415,000 unique locations from more than 11,000 globally distributed EnMAP L2A scenes collected over two years. Additionally, 17% of these locations include multiple timestamps, enabling multi-temporal HSI analysis. SpectralEarth data have been filtered for clouds and atmospheric artifacts. Further, the EnMAP tiles have been patchified into 128x128 spatial pixels. Additionally, three downstream datasets were constructed for land-cover and crop-type mapping, providing benchmarks for model evaluation. Downstream task data have been collected from the Europe’s CORINE land cover dataset and the United States agriculture and land cover products CDL and NLCD, respectively. The SpectralEarth dataset can be downloaded through the EOC Geoservice . More information about the dataset is available here.
Additionally to the EOC Geoservice, also users of the EO-Lab platform can access the EnMAP L2A ARD data collection as well as the SpectralEarth dataset. This is made possible through identity federation between the two platforms. EO-Lab offers easy discovery, access to data, and it provides processing options for platform users.
