Explosive eruption of Mt. Redoubt, Alaska on 23rd March 2009
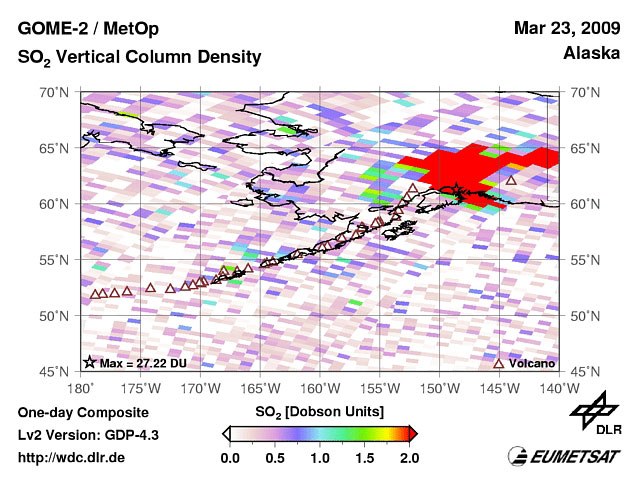
After an inactive phase of 20 years Alaska’s Mount Redoubt volcano erupted explosively on 23rd March 2009 at 5:38 UTC. Four further eruptions followed. Each of these eruptions lasted 4 to 20 minutes and sent ash clouds up to 15 - 18 km. The ash has been moved northward due to the wind direction. For safety reasons Alaska Airlines cancelled 19 flights out of Anchorage, the most populous city in Alaska.
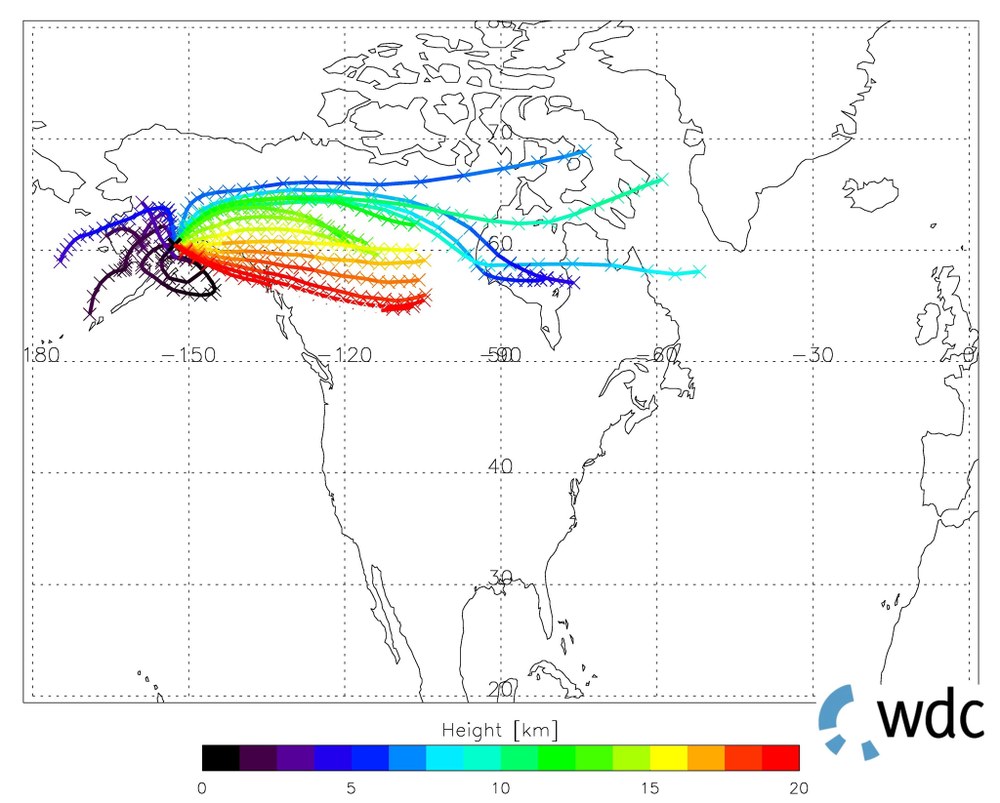
Measurements of the GOME-2 (Global Ozone Monitoring Experiment) instrument on board MetOp reveal large amounts of sulphur dioxide (SO2) ejected by the volcano (Figure 1). As part of a volcano activity monitoring service DLR-DFD provides forecasts of the time-spatial distribution of the volcanic ash and SO2-cloud. Figure 2 shows a 60 hours forecast based on forward trajectory ensembles started between 0 and 20km above sea level. Three days after the first eruption ash particles and trace gases that have been lifted up above 15km will reach the middle of the state Alberta, Canada.
Mount Redoubt volcano is still unstable and further eruptions are expected.
