MASCOT
Timeline | |
|---|---|
Launch of Hayabusa2 spacecraft: | 3 December 2014 |
Health check of the MASCOT lander: | June 2015 |
Calibration of MASCOT instruments: | September 2015 |
Earth fly-by: | December 2015 |
Health check of the MASCOT lander: | July 2016 |
Calibration of MASCOT instruments: | November 2016 |
Health check of the MASCOT lander: | May 2017 |
Calibration of MASCOT instruments: | November 2017 |
Health check of the MASCOT lander: | Spring 2018 |
Hayabusa2 arrives at asteroid: | 27 June 2018 18-month long stay |
MASCOT lands on asteroid Ryugu: | 3 October 2018 |
Hayabusa2 collects samples of the asteroid during a short ground contact (possibly several times): | 2019 |
Hayabusa2 to depart from asteroid: | November/December 2019 |
Hayabusa2 to arrive at Earth: | Late 2020 |
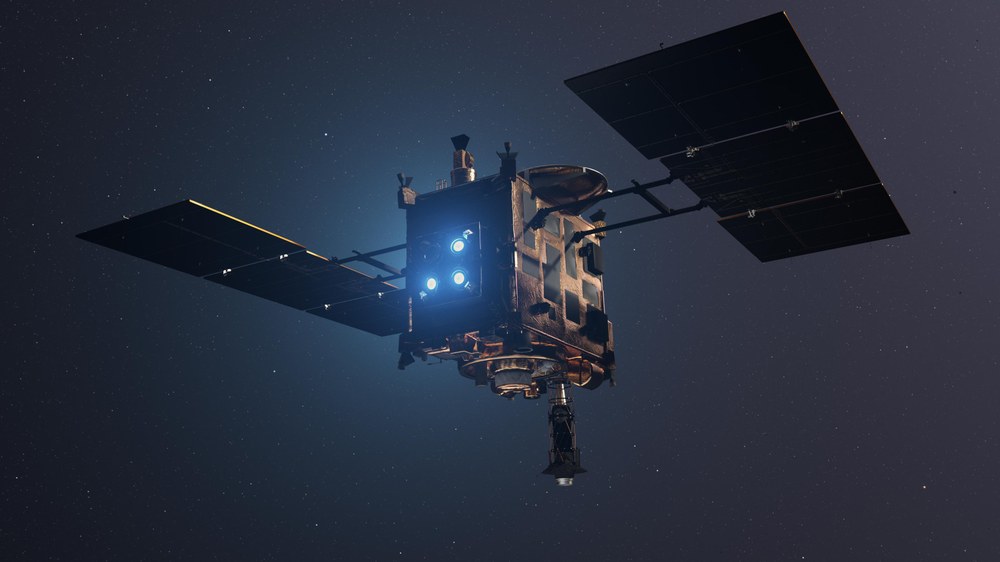
Hayabusa2 spacecraft, Specifications/Instruments | |
|---|---|
Type of mission : | Asteroid sample return mission |
Operator: | JAXA |
Launch date: | 3 December 2014, 04:22 UTC |
Launch site: | Yoshinobu Launch Complex, Tanegashima Space Center |
Rocket: | H-IIA 202 (Flugnummer F26) |
Mission length: | 6 years, return planned for December 2020 |
Mission control centre: | JAXA SSOC (Sagamihara Space Operations Center) |
MASCOT control centre: | DLR Microgravity User Support Center (MUSC) |
Startmasse: | approx. 600 kilograms |
Hayabusa2 spacecraft, key features | |
|---|---|
Electric Propulsion System (Ion engine): | Used for changing orbit during journey to asteroid as well as return to Earth; engine is energy-efficient, with one tenth of power consumption compared to chemical propellant. |
Sampler mechanism: | SMP to collect samples from surface of asteroid. Cylinder-shaped sampler horn will be lowered to surface, shooting out a small projectile once it makes contact with the surface. Materials ejected will then be collected via a catcher. |
Target markers: | Five beanbag-type markers will descend to the asteroid's surface to serve as artificial landmarks prior to landing for the distance measurement of the collision warning system. The target markers are hollow and filled with a granulate that dampens the kinetic energy and thus prevents them from bouncing from the surface. |
Re-entry capsule : | Container that stores samples from asteroid and will re-enter Earth’s atmosphere at 12 kilometres per second. |
Hayabusa2 spacecraft, mission instruments | |
|---|---|
Small Carry-on Impactor (SCI): | Two-kilogram copper lump to collide with surface of asteroid to make an artificial crater, used to study the inside structure of the asteroid before and after impact; will also be used to sample 'fresh' material underground. |
Near InfraRed Spectrometer (NIRS3) and Thermal Infrared Imager (TIR): | Remote sensing instruments to measure asteroid from Hayabusa2’s 20 kilometre-distance position. NIRS3 will investigate mineral and water metamorphism; TIR to study temperature and thermal inertia of asteroid. |
MINERVA-II: | 2 small rovers that will study the asteroid from its surface. |
MASCOT: | Small lander designed to study the asteroid using four observation devices and move across the asteroid. |
MASCOT lander specifications/Instruments | |
|---|---|
Dimensions: | 295 mm x 275 mm x 195 mm |
Weight: | 9.6 kilograms |
Target asteroid: | 162173 Ryugu |
Mother craft: | Hayabusa2 |
Operators: | DLR, CNES, JAXA |
MASCOT lander instruments | |
|---|---|
MASCOT Camera (MASCAM): | Wide-angle camera that takes pictures during the descent to the asteroid surface and will provide ground data for the instruments on board Hayabusa2 as well as contextual information for the instruments on board MASCOT. (Institute of Planetary Research, DLR) |
MASCOT Radiometer (MARA): | The radiometer is used for the high-resolution determination of the surface temperature as well as the thermal changes during the day-night changes on the asteroid. (Institute of Planetary Research, DLR) |
Magnetometer (MAG): | Determination of the asteroid's magnetic field (Institute of Geophysics and Extraterrestrial Physics, TU Braunschweig) |
Infrared spectrometer (MicrOmega): | Determination of the mineralogical composition of the asteroid surface. (Institut d'Astrophysique Spatiale, Université Paris Sud) |
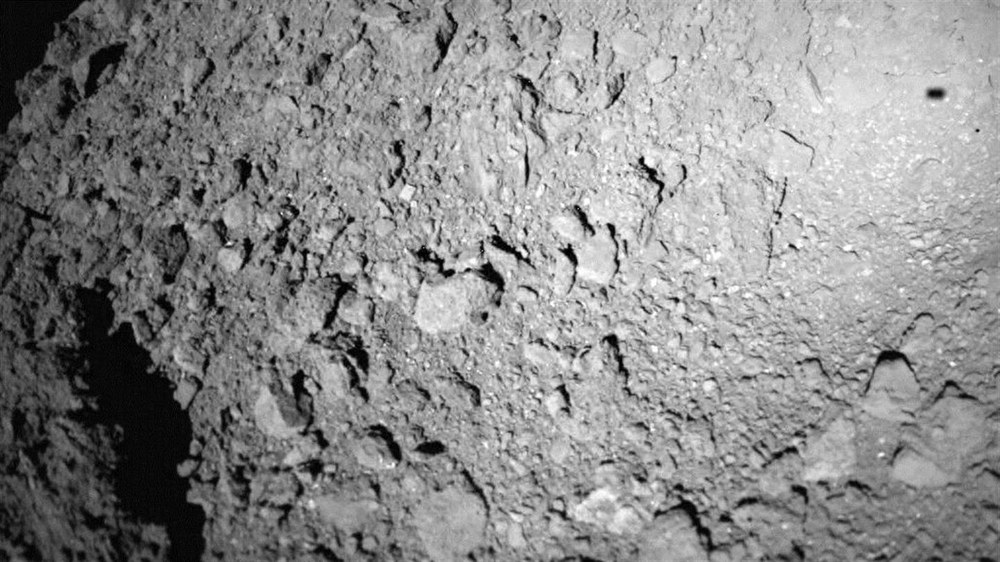
The target: Asteroid (162173) Ryugu (formerly 1999 JU3) | |
|---|---|
Origin: | C-class asteroid (carbon-rich), near-Earth asteroid of the Apollo group |
Discovery: | May 1999 |
Discoverer: | LINEAR (Lincoln Near Earth Asteroid Research) Team |
Shape: | Approximately spherical with the irregularities expected in small bodies (determined by thermal observations. |
Diameter: | 880 ± 15 metres |
Rotation period: | 7.6 hours |
Albedo: | 0.05 (very low, darker than coal) |