S2TEP

With the S2TEP small satellite platform, DLR has an independent platform for conducting its own technology experiments under space conditions. The satellite bus is based on modular and scalable technologies developed at DLR. Only through in-house research and development in the area of central avionics components can the rapid and cost-effective implementation of S2TEP-based missions and adaptation to a wide range of user requirements be guaranteed.
Satellites enable global communication and navigation services. Through its further development, DLR space research is making an important contribution to the digitalization and mobility of the future. In order to advance research for space travel and its applications, DLR has defined the framework for its own experiments in space: the DLR satellite strategy provides for the launch of a satellite weighing 20-50 kg (S2TEP) every 2 to 3 years and one weighing around 200 kg (COMPSAT) every 5 to 6 years. Ongoing satellite projects, which are carried out regularly with these two platforms, make significant contributions to DLR's scientific excellence by:
- looking at all elements of a space mission (satellite bus, payload, ground segment and space transportation), driving innovation there and thus sustainably improving DLR's end-to-end system competence
- provide independent access to space-based research and development for DLR and achieve autonomy with regard to the otherwise existing dependence on third-party satellite missions
- promote interdisciplinary cooperation between DLR institutes and exploit synergies
- invite DLR-external institutions and industrial partners to national and international collaborations.
The idea behind S2TEP
The subsystems of a satellite are often mission specific developments; this limits the ability for reuse in other missions, and makes adaptations to new requirements difficult. To streamline this process, DLR is developing its own satellite platform, designing main avionic components that are easily adaptable; and at the same time utilizes the latest research and technology.
The platform also offers a higher degree of flexibility; enabling short-term design adjustment; as well as the ability to adapt essential cost drivers and shorten the development time.
S2TEP development focus
The S2TEP avionics introduce a variety of innovative features; a modular and flexible architecture; as well as novel design and verification processes like:
- Scalable on-board computer (in terms of essential parameters such as computing power, reliability, interfaces and communication capabilities)
- Model Based Software Development & Auto coding
- Software Defined Radio
- Scalable power systemDecentralized operation concept with a high degree of autonomy
- Simulation & automatic verification
Model based design process (Model Based Systems and Software Engineering, Space 4.0)

The DLR developed avionic components will be flown on S2TEP as either technology demonstrations or bus components, depending on their degrees of maturity.
S2TEP based missions will offer an ideal test environment for technology demonstrations and research within the field of avionics, and thus contributing significantly to the gain of comprehensive and deep design understanding within this field.
S2TEP technology exchange
The technologies developed for S2TEP are also used on the COMPSAT platform; their high degree of scalability creates a synergy between both platforms; enabling technology exchange and allows for a high degree of reusability.
Technologies which are flown on COMPSAT as secondary payloads can later be flown on S2TEP as critical bus components, and vice versa, making both platforms test beds for new developments.
To maintain a high level of flexibility, on both component and system level, the research and development work is focused mainly on scalability in terms of performance, adaptability and reliability. The S2TEP philosophy is further explained below, using two of the developed technologies as examples; the modular software platform and the scalable on-board computer.

Scalable On-Board Computer
The Compact On-Board Computer (COBC) is easily adaptable and can be customized to fulfil a large range of control and data processing requirements. The generic design of the computer facilitates the usage of electric components of different qualification levels, adds the ability to change processor performance, memory size and type, as well as the number and type of interfaces. The on-board computer will be flown on the first COMPSAT satellite Eu:CROPIS as a technology experiment, and after in-orbit verification, on S2TEP as part of the bus, and on the second COMPSAT mission as the payload computer.
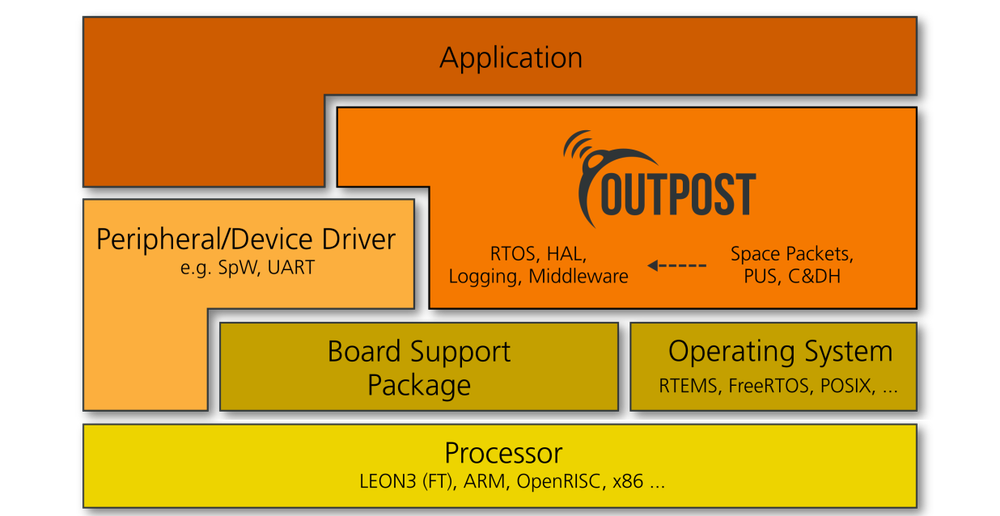
Modular software platform

The Open modUlar sofTware PlatfOrm for SpacecrafT (OUTPOST) was originally developed for the on-board computer COBC, but is now also being used for the S2TEP and COMPSAT platforms, as well as in sounding rockets and launchers.
The usage of abstraction layers, towards hardware and operating system, creates a strong foundation for modular and portable implementations of flight software.
The key elements of OUTPOST have been released under an open-source license; available to private and industrial users, for possible joint further developments.