We start with AM-compatible component design (DfAM), the qualification of materials and material combinations and intelligent process planning, through to monitoring the manufacturing process and integrated quality assurance. In addition, FLAME's integrated laboratory for automated material card derivation for crash simulation enables us to quickly qualify materials mechanically and simulate additively manufactured components. We also integrate production data and in the form of a digital component twin in order to best predict performance.

We focus on two technologies in the field of thermoplastic additive manufacturing processes:
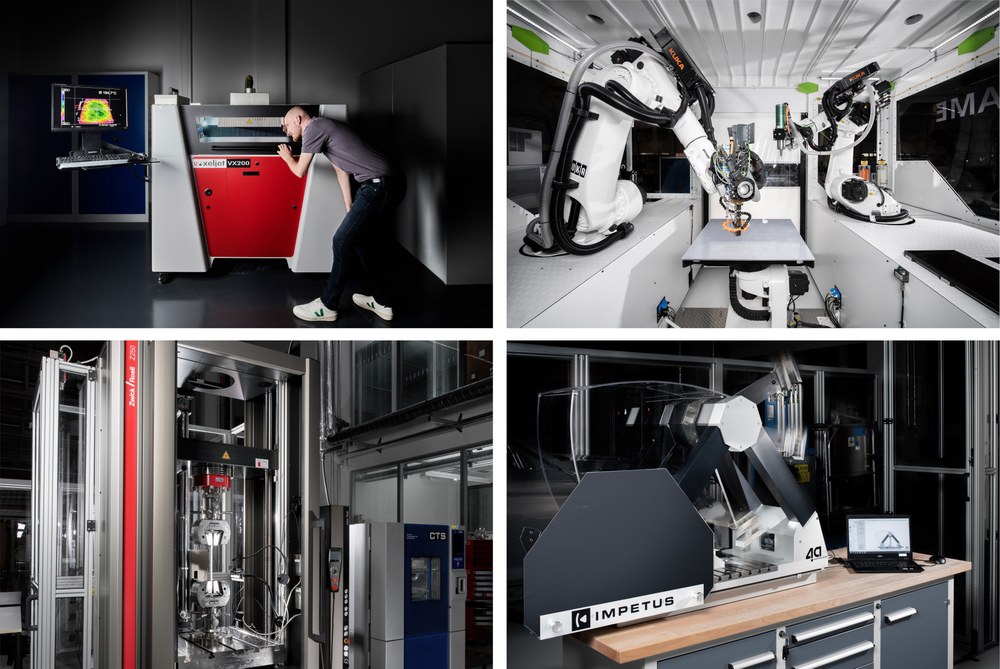
The High-Speed Sintering process (HSS) (link to HSS page) is a powder bed-based additive manufacturing process for polymers. The process principle enables fast, tool-free generation of complex structures from prototypes to small series parts. The system used at the DLR Institute of Vehicle Concepts is the Voxeljet VX200 HSS. In contrast to other powder bed processes, an infrared lamp is used here as the energy source, whereby the differentiation between areas to be sintered and areas not to be sintered in each layer is realized with the help of an additionally introduced ink.
Robotic Screw Extrusion Additive Manufacturing (RSEAM) is a novel extrusion 3D printing process used in the Yizumi SpaceA hybrid manufacturing cell. The system enables the processing of cost-effective standard granulates with high build rates and combines the possibilities of additive manufacturing using SEAM with subtractive machining and the ability to handle components in a flexible unit. It especially allows for the fast manufacturing of large additive and hybrid parts with high fibre volume contents for semi structural vehicle components
Further information on the technologies mentioned can be found on the respective technology page of the research infrastructure of the DLR Institute of Vehicle Concepts. If you are interested or have any questions, please do not hesitate to contact us.

