HPDA basic software project
Large amounts of data alone are not enough to make predictions. Only by analysing the data sets for patterns, structures and regularities is it possible to extract useful knowledge from data. For data analysis, classical statistical and numerical methods are used on the one hand, and intelligent analysis methods from the field of machine learning on the other. The ever-increasing amounts of data lead to a problem in data analysis. Basic software for High-Performance Data Analytics (HPDA) is to enable the evaluation of such data volumes.
Joint software platform at DLR
The HPDA basic software project creates a common software platform for the analysis of large scientific data sets at the German Aerospace Center (DLR). To this end, the platform provides basic algorithms for statistical and AI-based data analysis, numerical linear algebra and fast I/O libraries for large parallel computer systems and fast data storage systems.
A large part of the Big Data application software at DLR is parallelised and optimised separately and at great expense for the mainframe computers available. Due to interfaces coordinated with DLR users within the analysis platform created in the project, collaboration across application boundaries will be significantly facilitated.
The aim of our project is to develop a jointly used software platform for Big Data applications. This application platform forms an intermediate layer between the application and the HPDA or HPC system.
Due to the breadth of applications, the application platform will necessarily consist of several libraries, which will be further developed with regard to the use of common interfaces. The concrete applications will be adapted to the basic software so that the time-consuming application parallelisation is ideally already completely covered by the basic software.
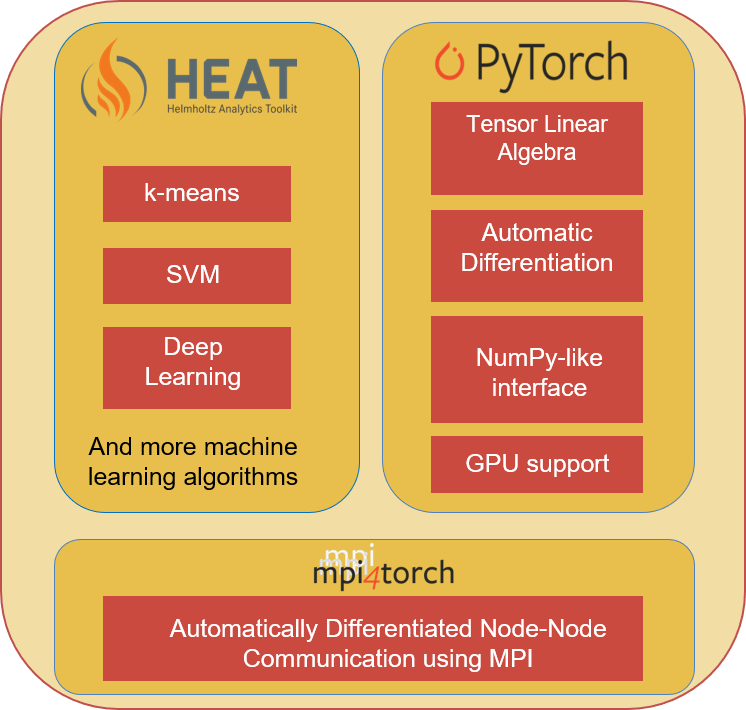
Heat is internally based on the open source software PyTorch, which is developed for machine learning. Heat extends the software with the aspect of data parallelism for mainframes of high-performance computing, using mpi4torch. The highly parallel algorithms support various Helmholtz applications in data analysis, for example in the area of high-speed images of rocket engines.
Software libraries of the HPDA basic software project
Project runtime:
- Since 2022
Scientific participants:
Publications on this project on eLIB:
- HeAT - a Distributed and GPU-accelerated Tensor Framework for Data Analytics
- An Optimized, Parallel Computation of the Ghost Layer for Adaptive Hybrid Forest Meshes
- t8code - Extreme Scale Adaptive Mesh Refinement with Arbitrary Elements
- Scalable algorithms for adaptive mesh refinement with arbitrary element types
- Modularity of Lowlevel Forest-of-octree Libraries
- Lossy compression by adaptive mesh refinement
- Exascale-ready adaptive mesh refinement and applications in Earth system modelling
- Enabling dynamic adaptive mesh refinement (in MESSy) using t8code