Digital Atlas 2.0
A digital transformation is advancing worldwide and is affecting the areas of transportation infrastructure, energy supply and urban planning. In this digital transformation, geodata, as well as their processing and validation, play a cross-domain role and are increasingly becoming part of our everyday lives. Use cases range from map generation for our navigation system, over automated driving assistance systems, to complex noise dispersion simulations that can influence urban planning. All of these use cases require that different types of geospatial data can be efficiently acquired, processed, and validated.
Within the scope of Digital Atlas 2.0, eleven DLR institutes and facilities are developing and implementing concepts to integrate these heterogeneous data sets into a uniform geodata infrastructure across domains and to make them available to applications via standardized interfaces. The project partners are concerned with the acquisition, processing, validation and provision of these data in a common catalog.
Augemented Reality assist in the validation of geodata sets
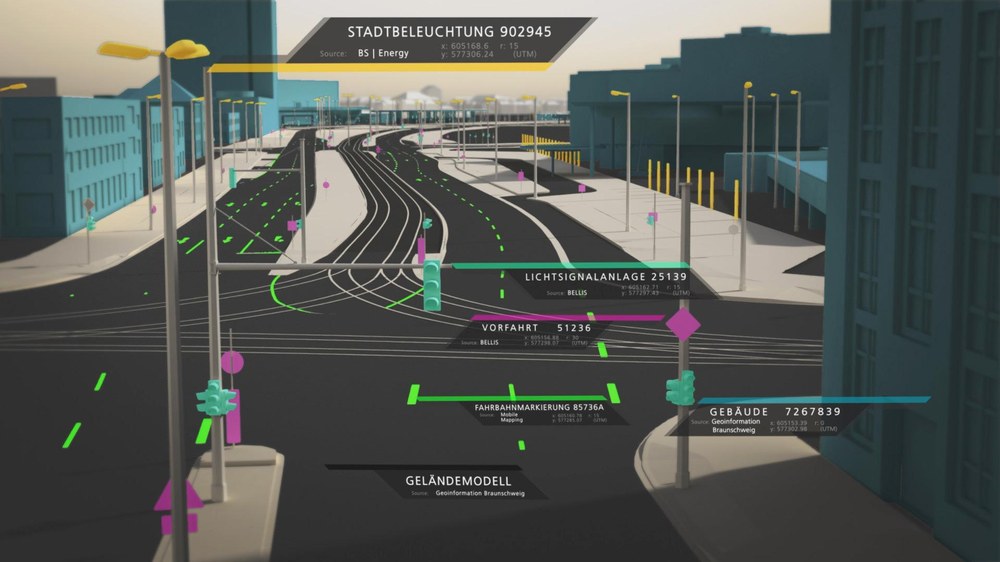
The DLR Institute of Software Technology concentrates on the validation of existing geodata sets. The focus is on georeferenced traffic infrastructure data, such as sign datasets. These datasets describe where exactly which type of traffic sign is located and how it is oriented. This information is particularly important with regard to autonomous driving vehicles, as such datasets could be used as additional data source. This assumes that the data sets are correct.


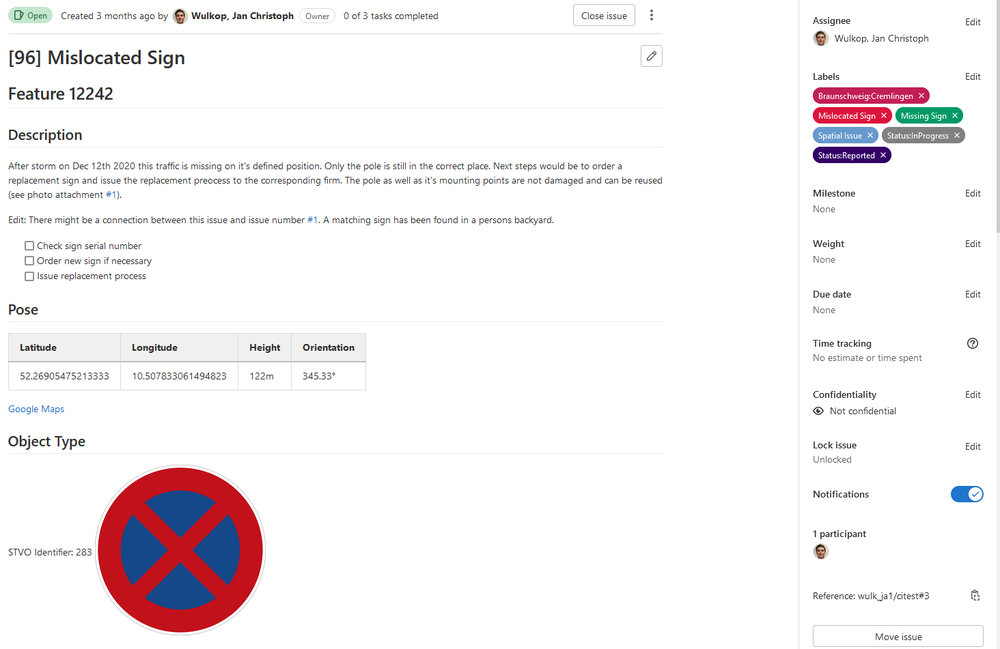
In reality, however, discrepancies can occur between the signs in the datasets and the real signs, whether due to vandalism, storm damage, or human error in the construction of the signs. These discrepancies between target and actual conditions must be found and corrected. The Institute for Software Technology is researching and developing concepts for this purpose, using modern augmented reality approaches to superimpose the nominal condition directly over the real environment, thus making it easier to detect errors in the data sets.
By using mobile augmented reality devices, experts can report an error directly via the device on site and store it in a database so that appropriate steps can be taken to correct it. An interactive 3D visualization, as well as machine learning approaches for automated recognition of the real signs are used to facilitate the work of the experts.
Project runtime:
- 01/2022 – 12/2025
Scientific participants:
- DLR Institute of Transportation Systems (Project lead)
- DLR Institute of Software Technology
- DLR Microwaves and Radar Institute
- DLR The Remote Sensing Technology Institute
- DLR Institute for the Protection of Maritime Infrastructures
- DLR Institute for the Protection of Terrestrial Infrastructures
- DLR Institute of Systems Engineering for Future Mobility
- DLR Institute of Transport Research
- DLR Institute of Networked Energy Systems
- The German Remote Sensing Data Center
Publications on this project: