Mars Express
Mission | |
|---|---|
Launch: | 2 June 2003, 19.45 CEST |
Arrival in Mars orbit: | 25 December 2003, 04.00 CET |
Launch site: | Baikonur, Kasachstan |
Launcher: | Soyus/Fregat |
Ground stations: | Perth (Australia), Kourou (French Guiana) |
Operational times: | 6.5 - 7 hours per day |
Mission Control: | European Space Operations Center (ESOC), Darmstadt |
Nominal mission: | 1 Mars year (ca. 2 Earth years ~ 687 days); because of its enormous scientific yield, ESA has extended the Mars Express mission several times, with the most recent extension lasting until 2026. |
Orbit type: | Ellipse, Final orbit: 250 km (closest approach to Mars) x 11.583 km (furthest point from Mars); Inclination 87 degrees; Orbit period 7.5 hours |
Spacecraft | |
|---|---|
Launch mass: | 1042 kg (427 kg fuel) |
Scientific payload: | Orbiter 116 kg, Lander 60 kg |
Dimensions: | Orbiter 1.5 m x 1.8 m x 1.4 m; Solar arm mit 12 m width, Surface area 11.42 sq metres |
Energy supply: | Orbiter: Solar arm: Si-cells, 660W with 1.5 AE; Energy storage 3 Li-Ion batteries, Overall capacity 64.8 Ah; Power supply 28 V; Maximum performance 450 W |
Data communication: | X-band (7,1 GHz) and S-band (2,1 GHz). Communication: omnidirectional low-gain antenna (LGA), 4 m; directional high-gain antenna (HGA), 1.8 m; 2 di-pole antennas, both 20 m |
Propulsion: | 8 engines for orbit corrections, each can thrust 10 Newtons; 1 master engine for braking in Mars orbit, thrust 400 Newton; stabilisers |
Instruments Orbiter | |
|---|---|
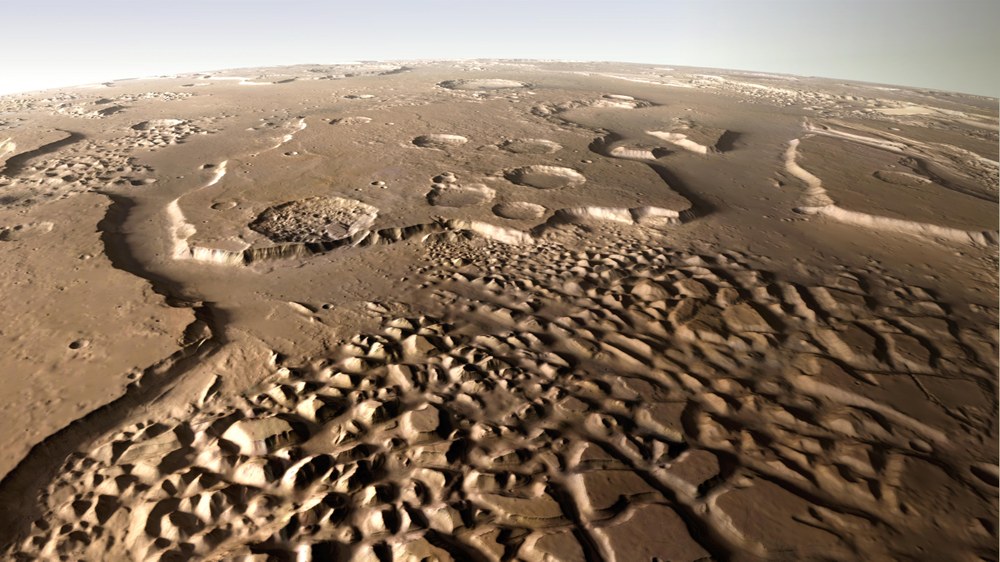
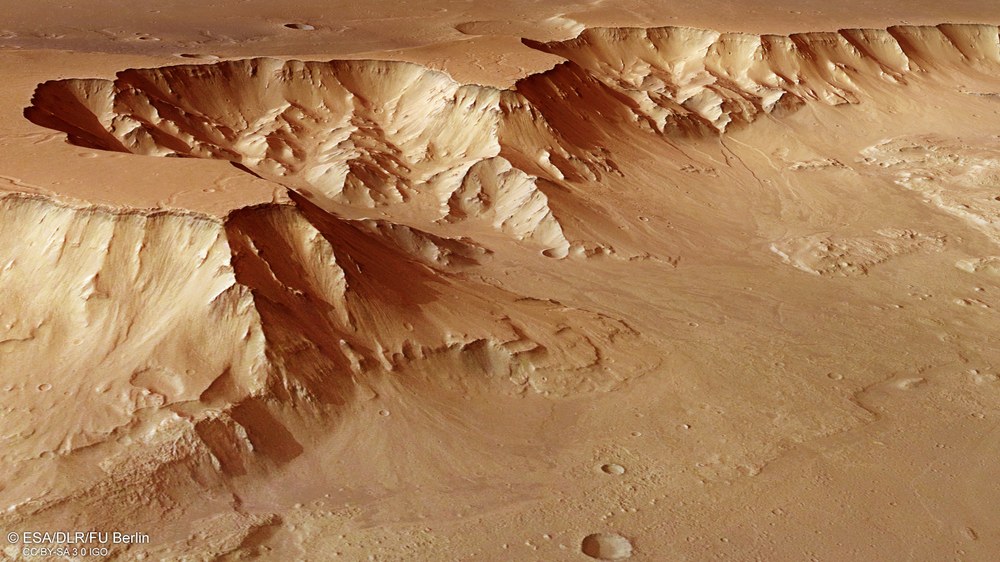
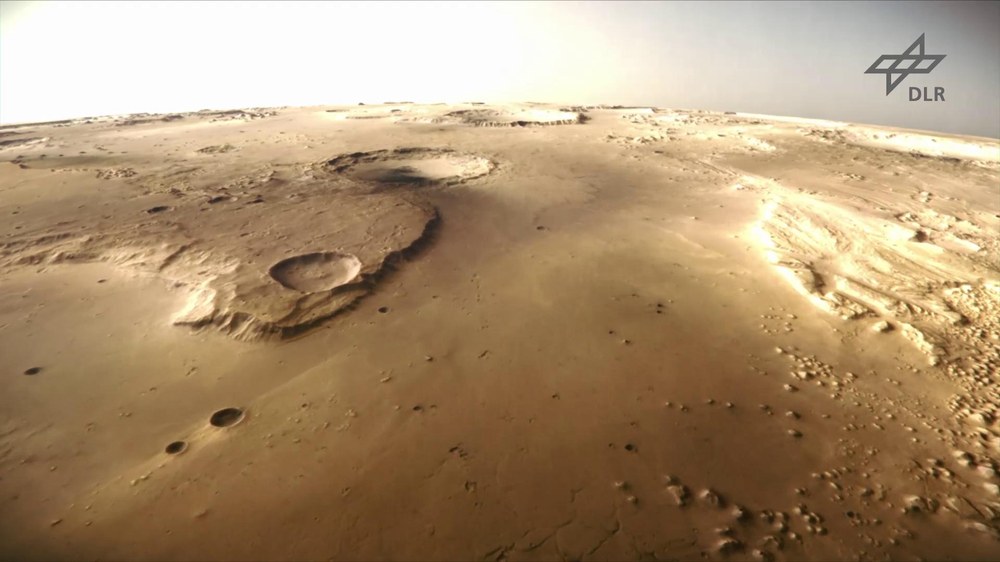
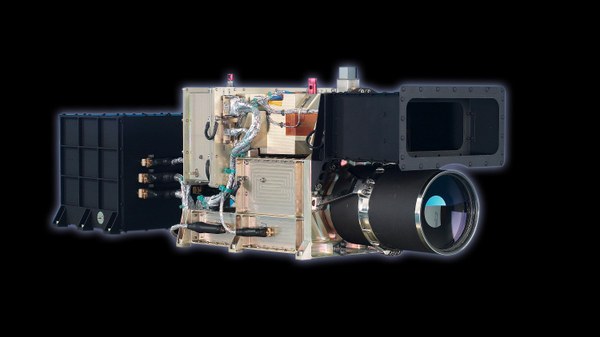
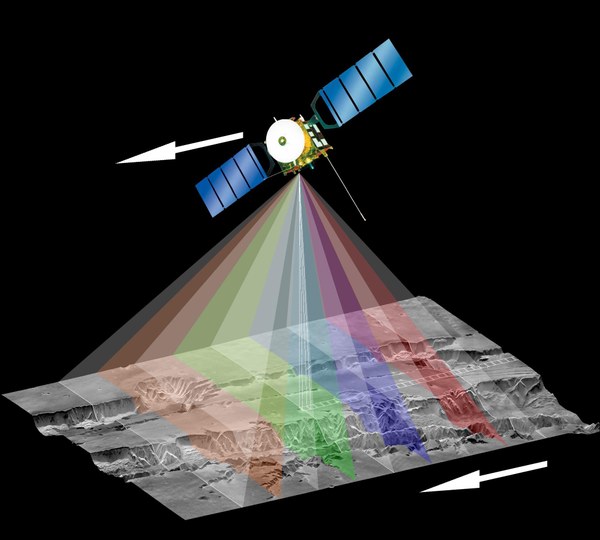
HRSC (High-Resolution Stereoscopic Camera) | German-led project: Study of the atmosphere, surface and gravitation |
MaRS (Mars Radio Science Experiment) | German-led project: Study of the atmosphere, surface and gravitation |
PFS (Planetary Fourier Spectrometer) | Italian-led project; German participation: Infrared spectrometer for the investigation of the atmosphere |
ASPERA (Analyser of Space Plasmas and Energetic Atoms) | Swedish-led project: Analysis of the reciprocal effect of the Mars atmosphere with the interplanetary medium |
MARSIS (Mars Advanced Radar for Subsurface and Ionospheric Sounding) | Italian-led project: Investigation of the Martian soil depth and also the upper atmosphere |
OMEGA (Observatoire pour la Minéralogie, l’Eau, les Glaces et l’Activité) | French-led project; developed for the Mars-96 mission: Infrared spectrometer for the investigation of the surface composition |
SPICAM (Spectroscopic Investigation of the Atmosphere of Mars) | developed for the Rosetta mission: Ultraviolet spectrometer for the investigation of the atmosphere |