DLRmagazine 166 – Fetch and carry
New Mars missions and a fascinating plan to bring samples from the Red Planet back to Earth.
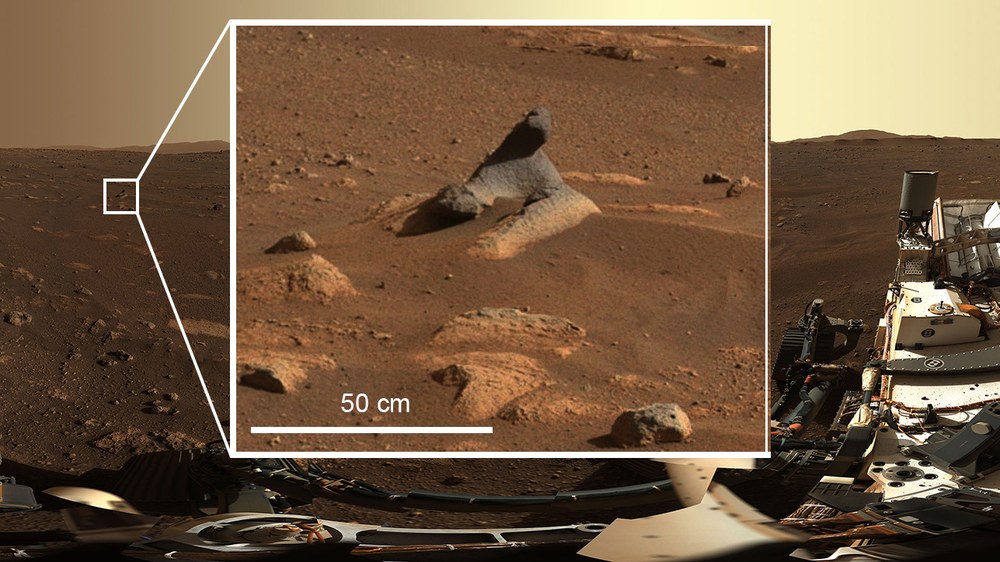



+++ NASA's Perseverance rover successfully landed in Jezero Crater on Mars at 21:55 (CET) on 18 February 2021.+++
Watch NASA's Perseverance Rover Land | Video from Mars!
Your consent to the storage of data ('cookies') is required for the playback of this video on Youtube.com. You can view and change your current data storage settings at any time under privacy.
NASA/JPL-Caltech/ASU/MSSS/NBI-UCPH
On 18 February 2021, NASA will initiate the most precise landing ever attempted on the Red Planet. A spacecraft with the Perseverance rover on board will enter the Martian atmosphere at around 21:38 (CET) at just under 19,500 kilometres per hour. Within seven crucial minutes, the spacecraft will decelerate to zero using its heat shield, parachute and braking thrusters to set the rover – suspended with cords – down in Jezero Crater at 21:45 (CET). Because the signal will take about 11 minutes to reach Earth from Mars, confirmation of the landing will arrive at NASA's control centre at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (Pasadena, California) at 21:55 (CET) at the earliest. The German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR) is represented on the Mars 2020 mission science team and will be involved in the evaluation of the data and images. Perseverance will search for signs of past life and collect rock samples that will eventually be returned to Earth by follow-up missions.
During the landing, sounds and high-resolution video recordings will be transmitted to Earth for the first time. NASA's most complex rover to date carries more cameras than any other interplanetary mission in the history of space exploration. There are 19 on the rover itself, plus four on other parts of the spacecraft that will collect footage of the entry, descent and landing. After landing and system checks, the first exploration of the surroundings will begin immediately. The 3D camera Mastcam-Z is programmed to record, process and transmit the first 360-degree panorama in 3D and in colour from a two-metre-high mast. All system components will then be tested over a period of several days before the scientific mission begins.
"During the first few weeks, the panorama will give us a view of a very special landscape – sediments in a former, ancient crater lake on Mars with a well-preserved river delta. Traces of past life could be found in its fine-grained deposits," says Nicole Schmitz from the DLR Institute of Planetary Research in Berlin. "From the very beginning, we have also had data processing tasks in the science team," adds Frank Preusker from the same Institute. "Most notably, we will use our many years of experience in processing stereo image data into digital terrain models." At maximum zoom, the camera can make objects the size of a housefly visible across the length of a football field in individual images. The scientific management of Mastcam-Z is carried out by Arizona State University.
Susanne Schröder from the DLR Institute of Optical Sensor Systems in Berlin is involved in analysing measurements from the SuperCam instrument. Led by Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico and IRAP/CNES in Toulouse (France), SuperCam makes it possible to determine the chemical composition and mineralogy of rocks, sand and dust in the rover's vicinity using lasers and without contact. Perseverance carries a total of seven scientific instruments. Scientists Jean-Pierre de Vera, Andreas Lorek and Stephen Garland from the DLR Institute of Planetary Research will be involved in the analysis of data from the Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA) instrument. MEDA uses a series of sensors to measure temperature, wind speed and direction, pressure, relative humidity, and the size and shape of dust particles. The scientific management of MEDA lies with the Centro de Astrobiología in Madrid (Spain).
NASA is breaking new technological ground with a helicopter drone named Ingenuity. For the first time in the history of space exploration, an aircraft carried from Earth will ascend from the surface of another planet into its atmosphere, attempt a controlled flight over the area and land again to repeat the experiment several times. Mars has less than one-hundredth of the atmospheric pressure on Earth, so Ingenuity had to be built to be extremely lightweight with very large, extremely fast-rotating rotor blades. The drone has a mass of 1800 grams and the rotor blades have a span of 120 centimetres. A miniature camera will provide images from a height of 10 to 15 metres.

DLR planetary research and NASA's Mars 2020 mission
Your consent to the storage of data ('cookies') is required for the playback of this video on Youtube.com. You can view and change your current data storage settings at any time under privacy.
©NASA/DLR
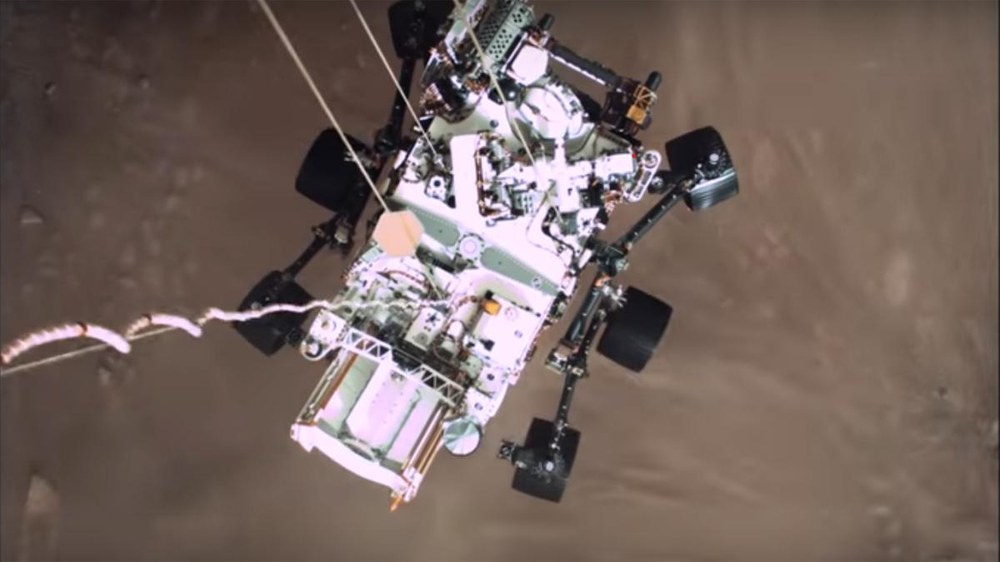
During entry into the Martian atmosphere, the spacecraft's protective shield will heat up to around 1300 degrees Celsius in three minutes. The 21.5-metre-diameter supersonic parachute will unfold about four minutes after entry at an altitude of approximately 11 kilometres and a descent speed of 1512 kilometres per hour. Twenty seconds after the parachute unfolds, the heat shield will be jettisoned and fall away, so that for the rest of the descent, a radar and cameras can compare information obtained in real time with stored maps and terrain models. A novel autopilot system will analyse possible landing sites in real time and compare them with the current position of the spacecraft to determine the final landing site on the surface of Mars. Until now it has never been possible to select the most accessible and – above all – safe landing target with such precision.
Approximately 2.1 kilometres above the ground at a descent speed of around 300 kilometres per hour, the hull will be jettisoned with the parachute and the landing thrusters will ignite. These will steer the spacecraft to the selected landing site and slow it down to 2.7 kilometres per hour at 20 metres above the surface. At this point, the landing stage will initiate the 'sky crane manoeuvre'. After unfolding its six wheels, the rover, which is the size of a small car and weighs 1025 kilograms, will be lowered from the 'sky crane', 7.6 metres below the landing stage on three unspooling nylon cords. When Perseverance reports ground contact and has landed in Jezero Crater, pyrotechnic cutters will sever the cords. The propulsion unit, which will remain airborne, will fly away before impacting the Martian surface at a safe distance. As a result of the signal transit times from Mars to Earth, the control centre at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in California will receive all status signals with a delay of approximately 11 minutes and will not be able to intervene in the automated landing procedure. During the landing phase, the 100-metre antenna operated by the Max Planck Institute for Radio Astronomy will be used. This fully steerable radio telescope is located in Effelsberg near Bonn, Germany. It will receive the signal from the Mars spacecraft at a wavelength of 74.7 centimetres, along with other receiving stations around the world, and make it available to NASA.
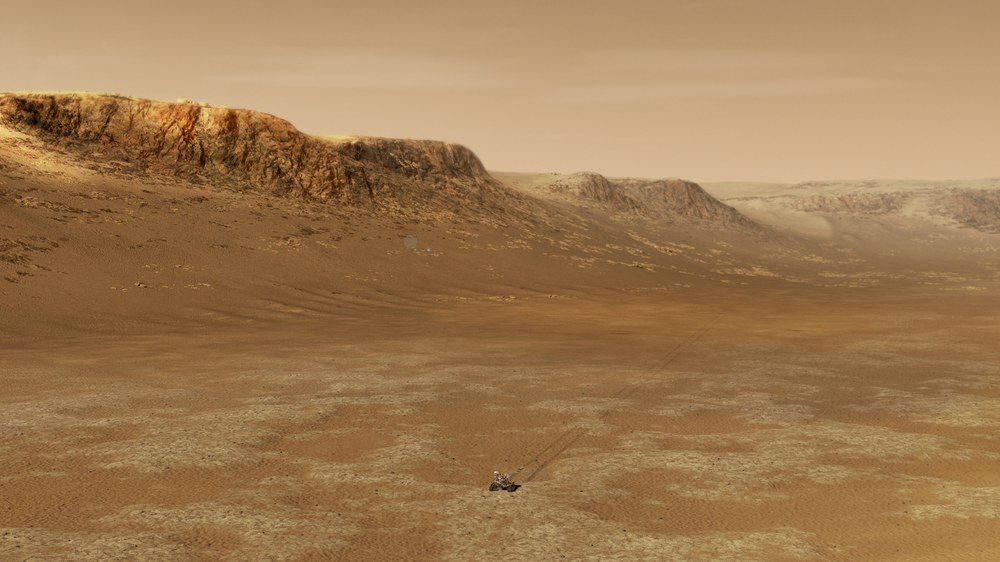
Selected after five years of deliberations, the 45-kilometre-wide Jezero Crater on Mars is a promising site to search for signs of past microbial life. More than 3.5 billion years ago, the now bone-dry basin was home to a body of standing water, a lake in which sediments deposited by two inflow channels have left a multiform river delta. Studies using the experiments on Perseverance could identify traces of past life in the sediments of the delta. In addition, for the first time in the history of Mars exploration, Perseverance is carrying 38 sample containers, which will be filled with cores from depths of up to 20 centimetres. These will be deposited at suitable locations across Mars for later return to Earth. Two future missions planned jointly by NASA and ESA will bring the samples – which are approximately the size of a pencil – to Earth in the early 2030s. On Earth, they will then be analysed in detail by researchers around the world using equipment that would be far too large and complex to send to the Red Planet.
Perseverance is the fifth rover that NASA has sent to Mars. In 1997, Sojourner landed on the Red Planet as part of the Mars Pathfinder mission and sent data and images to Earth for around three months. The twin rovers Spirit and Opportunity followed in 2004, covering longer distances for the first time, until the 2007 Martian winter ended communication with Spirit and a 2018 dust storm ended communication with Opportunity. In 2009, the Phoenix research station landed in the far north and in 2012, the Curiosity rover, whose chassis is identical to that of Perseverance, landed in Gale crater. In 2018, the InSight stationary landing platform touched down; InSight is a geophysical laboratory that explores the interior of the planet using, among other instruments, DLR's Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP³), which includes the self-hammering 'Mars Mole'. NASA's Perseverance rover is designed for a mission duration of one Martian year (roughly two Earth years) with the option to extend the mission.
Another rover is scheduled to embark to the Red Planet during the next launch window in 2022; this rover would also search for traces of past life. As part of the ExoMars programme of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Russian space agency Roscosmos, the Rosalind Franklin rover will, among other tasks, collect samples from a depth of up to two metres, bring them to the surface of Mars and perform high-precision analyses to look for biosignatures. Deep under Mars's surface, organic compounds are better protected from the destructive effects of cosmic radiation. DLR is contributing part of the scientific payload to Rosalind Franklin, including a high-resolution camera on the rover's mast that will allow researchers to analyse different rocks and determine the best possible locations for drilling.
