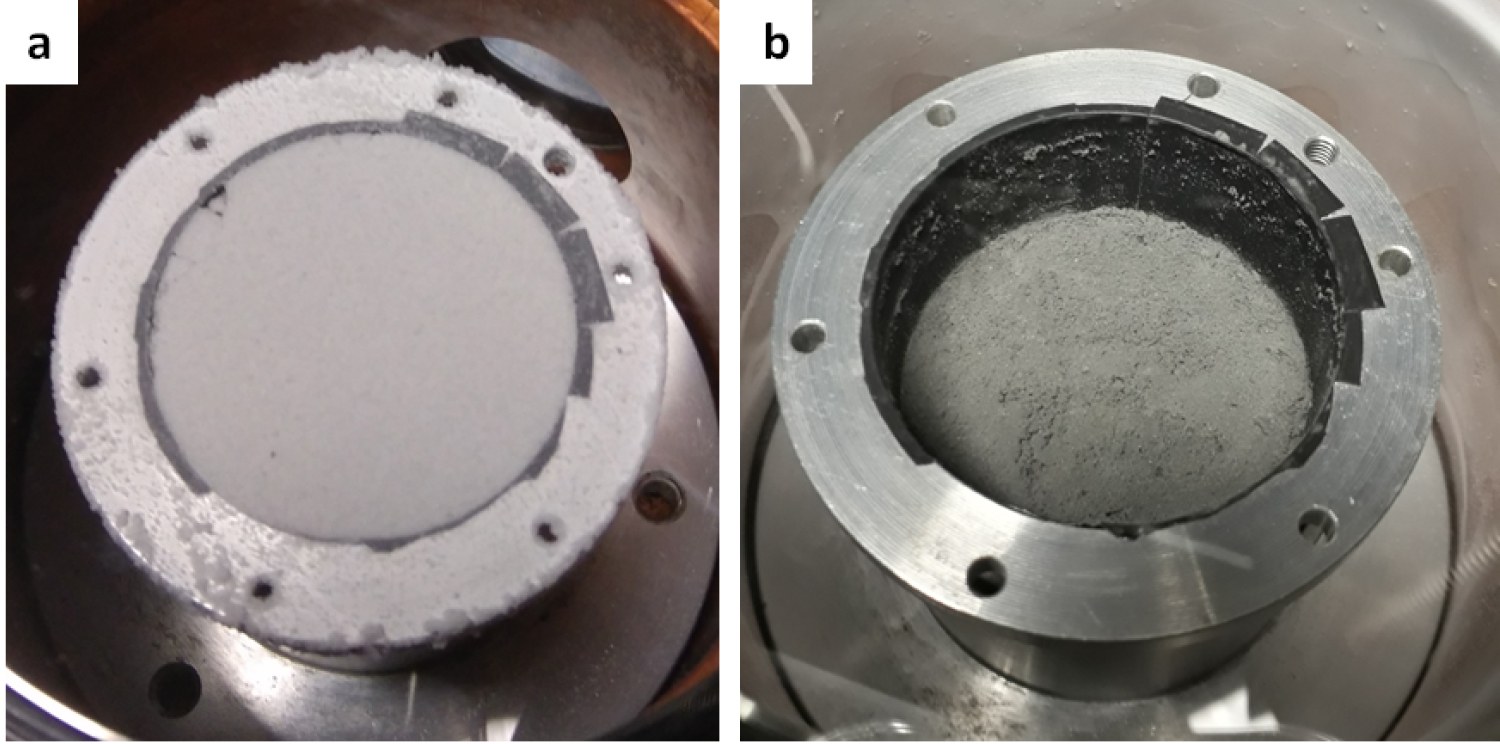
Sample container before and after the experiment
Sample container before and after the experiment
The image on the left shows the sample container filled with a mixture of ice and Ceres analogue material at the beginning of the sublimation experiment in the Cold Surface Spectroscopy (CCS) chamber at the University of Grenoble. It was filled with a mixture of Ceres analogue material developed at the Institute of Space Astrophysics and Planetology in Rome and cooled to a temperature of minus 100 degrees Celsius (173 Kelvin). The experiment was conducted under a high vacuum with a gas pressure of one millionth of a millibar for 133 hours. The ice sublimed completely, leaving behind a collapsed, highly porous, dust-like substance (right image). The cavity of the sample cylinder has a diameter of 4.8 centimetres.