Scenarios for radiative forcing now and in 2050
Scenarios for radiative forcing now and in 2050
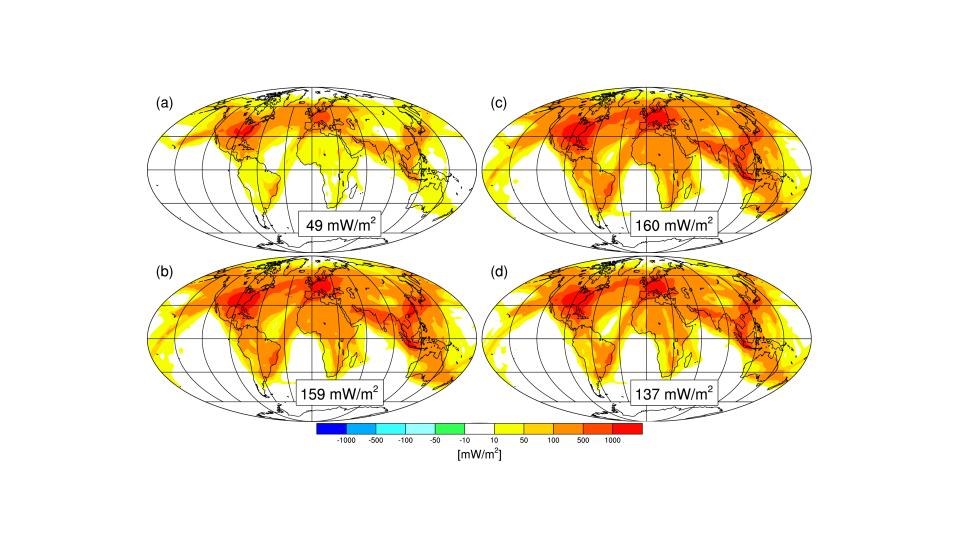
Radiative forcing caused by the formation of condensation trails for today’s climate conditions with (a) the current air traffic volume and (b) the predicted air traffic volume for 2050. The panels on the right show the radiative forcing for climate conditions expected in 2050 with (c) the air traffic volume for 2050 and (d) the air traffic volume for 2050 assuming an increase in fuel efficiency and a 50 percent reduction in soot emissions. Radiative forcing is a measure of the influence of a factor on the balance of incoming and outgoing energy in Earth’s atmosphere system. It is an index of the importance of a factor as a potential mechanism of climate change. A negative radiative forcing removes energy from the Earth system, leading to a cooling of the atmosphere. A positive radiative forcing supplies energy to the atmosphere, which heats up. Radiative forcing is expressed in units of watts per square metre.