Product comparison – sulphur dioxide cloud over Hawaii
Product comparison – sulphur dioxide cloud over Hawaii
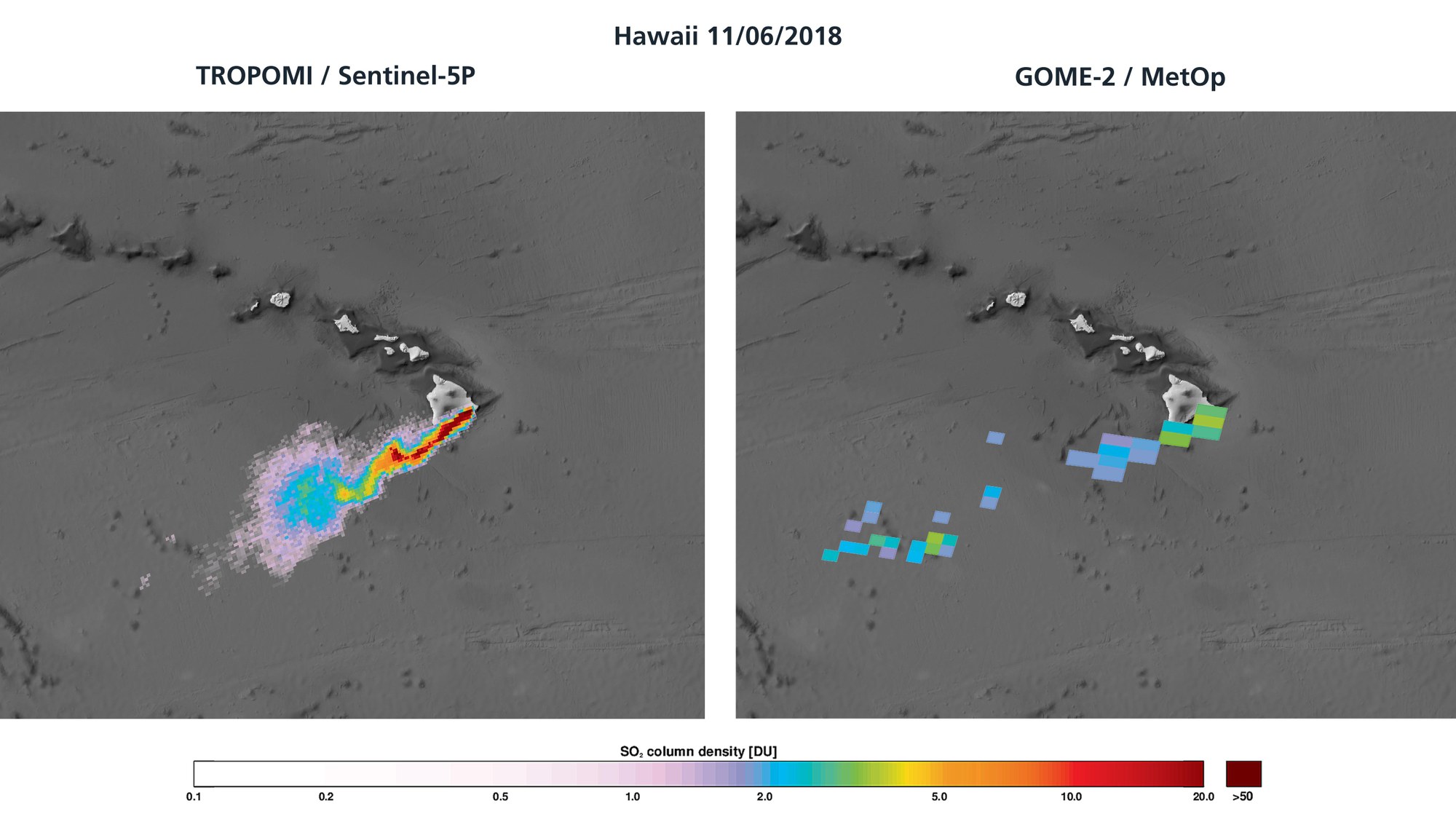
The high resolution of the new Copernicus satellite Sentinel-5 Precursor (S5P) allows, for the first time, the detection of closely separated sources and a more accurate determination of the propagation of volcanic ash clouds. The graphic shows the sulphur dioxide cloud over Hawaii after the eruption of the Kilauea volcano. On the left is the measurement result from the Sentinel-5P TROPOMI instrument, and on the right the result the GOME-2 instrument carried by the EUMETSAT MetOp A and B satellites. GOME-2 has a resolution of 40 × 80 kilometres, so that the distinction between multiple sulphur dioxide sources is not possible.
The image contains modified Copernicus Sentinel data (2018), processed by DLR / BIRA.