How the HRSC works
How the HRSC works
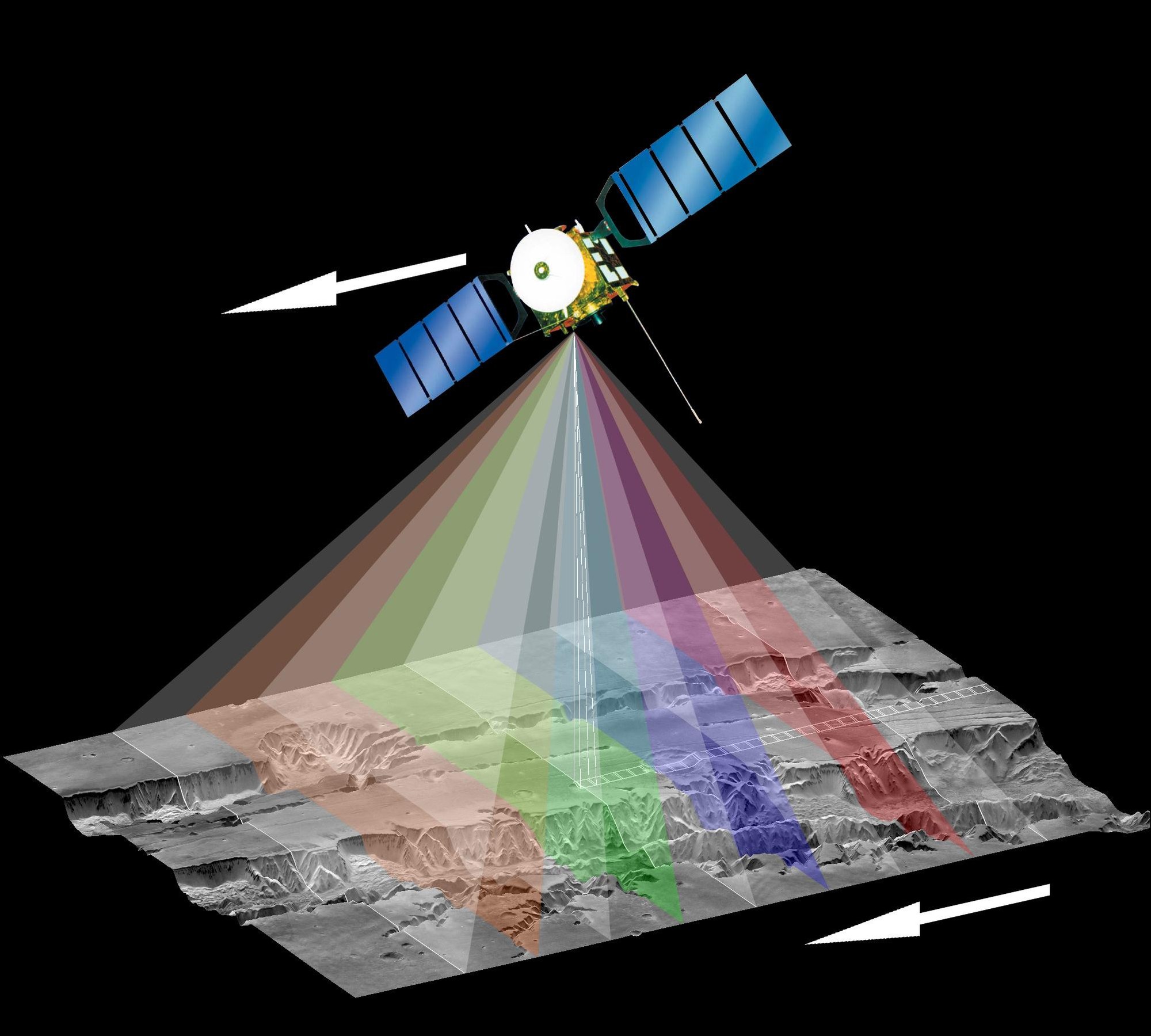
How HRSC works – nine light-sensitive sensor lines are installed in the HRSC, aligned transversely to the flight path. The camera moves across the planet, on board the Mars Express spacecraft. The surface is scanned line by line. To obtain stereo images, it is necessary to map the surface from a variety of viewing angles, which is why HRSC has more than one sensor line. In addition to what is referred to as the ‘nadir channel’, which scans the surface perpendicular to the spacecraft’s flight path, there are four lines directed forward along the flight path and four directed to the rear. Four of these eight lines are fitted with colour filters to produce colour images. This enables imaging of each point on the surface from nine different viewing angles. Computers are used to convert this data into elevation information.