µ-Computertomography (µ-CT)
The µ-CT of the DLR Institute of Engineering Thermodynamics in Oldenburg offers the possibility of analysing numerous materials. Samples are examined using X-rays, which enables non-destructive visualisation of the inside of the sample.

Research tasks
µ-CT is used for 3D imaging analyses of fuel cells, batteries, electrolysers and other technologies. Components such as electrode layers, gas diffusion layers or membranes can be analysed more closely. In this way, for example, degradation processes of the individual components after a test or the quality and reproducibility after production can be analysed.
Analysis
Various material properties can be analysed:
- Layer thicknesses
- Macroporosity
- Tortuosity
- Morphology
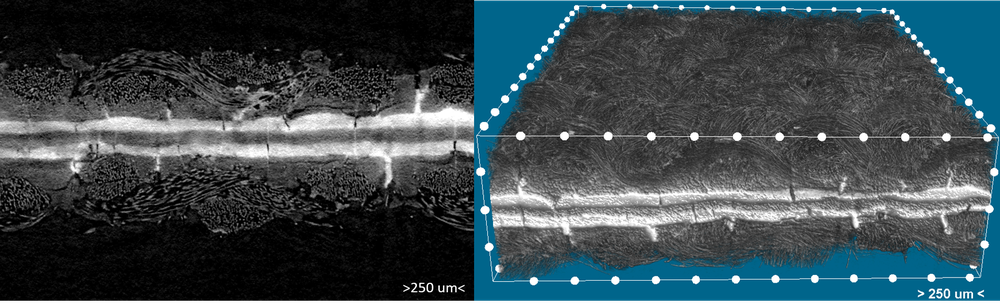
Visualisation of the sample
Shadow images of the sample are generated to create a 3D model. The 2D shadow projections form the basis for reconstruction into a 3D structure using the reconstruction algorithm. The optical reconstruction technique converts the shadow projections into cross-sectional images, which are stacked to form a 3D image volume. After reconstruction, the smallest volume units are referred to as voxels. This results in a variety of previously mentioned evaluation options.
