Resilienz
Cyber Physical Systems (CPS) are systems composed of microcomputers embedded within a physical system. CPS interact with their physical environment through actuators and sensors. Unlike traditional embedded systems, CPS are connected either to each other through interfaces or to the internet.
Future Cyber Physical Systems are smart, highly connected, and autonomous. They employ cutting-edge technologies such as AI-driven decision processes and Machine Learning to better perceive and interpret their surroundings. However, this leap in innovation also presents significant challenges. Departing from past practices means that established development and operational processes for such systems are outdated.
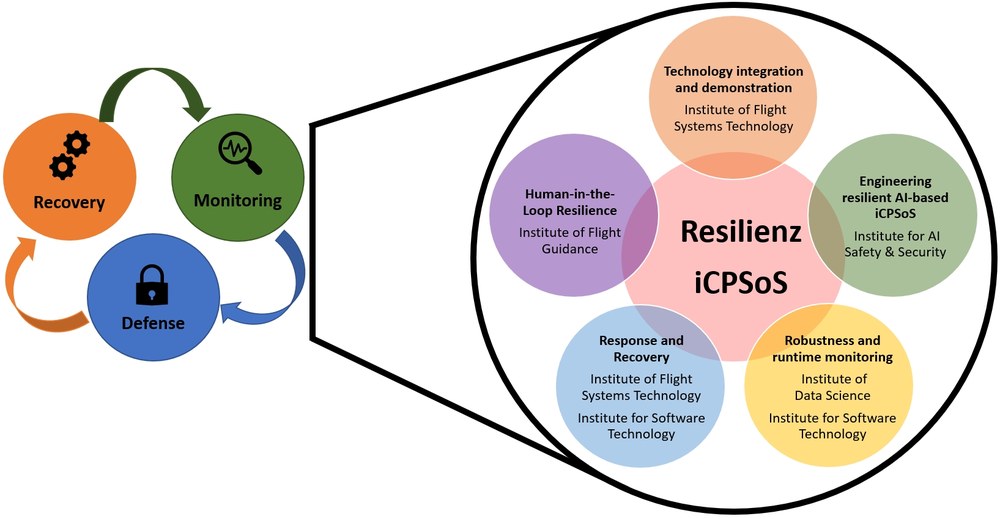
To ensure robust operation with minimized security risks despite increasing system complexity, we must redefine our understanding of security: Resilience is the key concept, offering a solution for the rapidly expanding attack surface. Resilient systems are designed to respond even in the case of malicious (or accidental) disruptions, aiming to restore the maximum achievable system function.
The Resilienz project follows a holistic approach. On one hand, algorithmic resilience mechanisms are integrated. These are algorithms that monitor the system and attempt to restore the full functionality of the CPS in case of disturbances. On the other hand, resilience at the system level is also considered, aiming to detect and address faulty behavior in the interaction of all connected components and operators. The developed mechanisms are then tested with sample applications of an aircraft computer and a human-machine interface within an air traffic controller scenario. The goal is to advance the current state of the art in resilient software, software development, fault tolerance, and anomaly detection.
The Institute for Software Technology researches new reconfiguration mechanisms for distributed systems within the "Resilience" project. This reconfiguration is intended to be performed within a hypervisor context. A hypervisor is a software solution that allows multiple software units to run in parallel and without disruption on a CPS. If one of the CPS were to fail, these subsystems should in turn be distributed to other CPS.
Furthermore, the Institute for Software Technology supports the exploration of possible data extraction points for anomaly detection and the integration of the software along with the prototype of the aircraft computer.
Project runtime:
- 2022 - 2024
Scientific participants:
Publications on this project: